Conference Lessons & Silver Linings: Should COVID-19 provide a push toward lasting change?

Last month, a group of researchers posted a thought provoking preprint entitled “Evaluating features of scientific conferences: A call for improvements.” As part of a client engagement with Morressier, Delta Think was fortunate to interview several of the authors (Drs. Sarvenaz Sarabipour, Humberto Debat, and Fiona Mumoki) about their findings and perspectives on conferences of the future. We were so struck with not only their research, but also their passion in support of the changes they recommend, that we thought it worth sharing the summary of our discussions and their insights. And while this research was begun well before COVID-19, their findings are perhaps more relevant than ever, as societies and conference organizers struggle with making content available in different formats and from virtual venues. Their insights offer our community food for thought as we assess not only current conference content dissemination but future conference program development and services.
Tell us about your article and the impetus for writing it. What prompted you to be advocates for early-career researchers in this space?
Sarabipour: For me, I’m an immigrant researcher, and I have not had access to many conferences. So, it was really important for me to advocate for greater access. I felt that last year was the time to do this as the situation has now changed for researchers, and there is an even stronger need to improve conferences. But even before then, improvements to meetings were long overdue. Early-career researchers face a number of issues, including accessibility to the location of conferences, funds, and gender and career stage equity. This is not an issue that is specific to researchers from the scientific hubs of the world. This inequality and inaccessibility is felt everywhere.
Mumoki: What attracted me to this initiative is the fact that I have experienced almost everything that we talked about in the manuscript. When coming from Africa, attending an international conference is really difficult. Conferences are very expensive to attend, but it’s even harder coming from Africa. Most researchers need to decide whether to use that money for a conference or for your lab. And if I get the opportunity to attend a conference, coming back to my home institute, sharing that information with others here is difficult, because we don’t have recordings of the speakers and there’s no poster to share with others. It then becomes difficult to pass on the knowledge I’ve learned from these meetings to colleagues. One other thing is that the meetings are normally very busy, so when you go there you want to network, you want to attend the symposia, so by the time you leave there, you’ve had to really pick carefully what you are going to attend.
Debat: I too have personal experience with the inability to access conferences. To attend a conference would be more than one year of fellowship salary for a student and the Institute doesn’t have the money to afford that. Those who do go to international conferences are the same few very well-known PI’s, so there is very limited participation in the scientific dialogue. The main goal of our manuscript is to try to focus on the democratization of knowledge using new technologies. Not only are conferences being done in the same way for the last 100 years, but in my opinion, they keep making the same mistakes in terms of inequalities and accessibility.
How do you think conferences should change, especially now in the midst of the pandemic?
Sarabipour: Obviously, researchers can’t go to conferences right now. But from what we see, only a few conferences have gone online and are going to happen virtually. We see a lot of people that haven’t been transforming to virtual meetings – they are just postponing to in-person meetings in 2021. We are not asking for conferences to just transform to virtual ones as they were. Alongside going virtual for environmental purposes and for accessibility, other issues that we discuss in our preprint could be resolved at the same time. We think the case of COVID-19 has brought a real shock to the scientific community, and I think it has made them think deeply about how conferences are held, the necessity of holding them so frequently, and their format.
Mumoki: That’s exactly it. I was to attend three meetings this year – one has been cancelled completely, and two have been postponed to next year, but none have become virtual conferences. However, technically speaking, apart from the cancellations, nothing has really changed. There are still groups that have difficulty physically accessing conferences, groups that don’t have the funds to attend. Actually, online discussion could be more beneficial than in-person discussion, which can be intimidating for early-career researchers especially who may be more comfortable engaging with other researchers by computer. In the article, we suggest platforms that can support chatting and break-out rooms, apart from the seminars that are held online. These can be much more inclusive. Diversity brings excellence to science, and researchers that enjoy conferences need to consider this.
Debat: When you do in-person conferences, you concentrate all the talks in a very narrow period of time. But in a digital context, you can relax that expectation and you can do a more continuous conference that can last weeks…It can promote discussion because you don’t have the time constraints that you have with in-person conferences.
As an Early Career Researcher, how do you disseminate work and promote yourself? What are the challenges?
Debat: We are advocates of the use of preprints. As a personal opinion, I usually try to disseminate our work as soon as we write it down and share it with the community to receive their feedback. This accelerates the dissemination of what we have studied, and at the same time, we are able to contribute to the scientific dialogue in a very public venue. In addition, in terms of conferences, I try to submit my presentations and slides to Zenodo and LinkedIn so anyone beyond the 50 people listening there can download it and see it. And I promote the use of Twitter. Anytime I am able to do it, I promote use of digital repositories and sharing places to try to disseminate more.
Mumoki: Something that I’ve been trying to do of late is create a personal website…I think it’s a nice way for me to consolidate everything that I’ve done in one platform. Also ResearchGate, I use that a lot in trying to disseminate my information, including conference information.
Sarabipour: Preprinting is very effective, having a personal website is very effective. Depositing all the preliminary material – talks, abstracts, manuscripts, data, into Zenodo or preprint servers across various fields. Personal website and Twitter. They are all very important and we discuss these in the manuscript in detail. These platforms are viewed by millions of researchers every month.
What message do you have for the research community?
Sarabipour: We really encourage researchers to read our preprint. We’ve taken great care in researching this and presenting our arguments, to show that there are deep rooted inequalities in how we present science. I would also like to encourage organizers of scientific conferences, universities, senior researchers, early-career researchers, and funding agencies to read this, in all continents, and think about it and have a dialogue about it. If they have data or statistics, they can add it to our database, which is openly available. We welcome all suggestions, feedback, and improvements moving forward. This is not a one-time effort.
Mumoki: As scientists, we always try to look for solutions to challenges that society is facing, so in this case we should practice what we preach. We should be open to change and open to learning new things and improving and making things better, so that the ones who are coming after us will not go through the same things that we are going through right now. We should put in the effort to make the changes that are necessary to move society forward, and this is one such way.
Debat: In-person conferences are very expensive. We analyzed 260+ conferences and calculated that people have spent $1.1 billion on them. To put that in perspective, that is the R&D research budget of Chile for a year. We are spending a lot on in-person conferences and questioning - what are we really getting out of that money? What could we do if we reallocated that money to scholarship or research itself?
Whether the ideas raised by these researchers and their preprint spark your interest or you are considering other strategic changes to your conference program, we are available to offer guidance and support to help you sort through the options and develop an approach that works best for your organization.






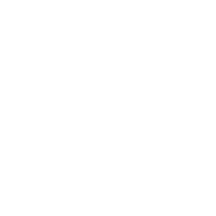
News & Views: Will cuts to National Science Foundation funding affect scholarly publishing activity?