Although it’s still not perfect, the data about scholarly output has improved over the last couple of years. We recently analyzed all 110m records in the Unpaywall data set to see if we could determine the uptake of OA at scale and set it in the context of non-OA output. The results might surprise you.
Background
Crossref is arguably the closest we have to an industry-standard article registry. Publishers can mark the articles they register in Crossref as “free to read” but there is no direct indicator about “permissive reuse.” Both conditions are needed for articles to be counted formally as Open Access. So further analysis of license types is needed to infer OA uptake. (And that’s assuming all publishers have deposited the relevant data in a timely and machine-readable way, which is by no means the case.)
The team behind Unpaywall1 have addressed these issues, and (in our view) done a terrific job of adding a meaningful Open Access status to the Crossref data. However, their method relies on inference and automated analysis. As they acknowledge in their most recent study,2 part of their method relies on identifying journals’ business models in order to adjust the OA status of the articles in them returned by their algorithms. As we’ve discussed previously, there is no definitive index of journals available; and those that focus on OA journals focus only on fully OA.
So, we still have an issue consistently and accurately categorizing articles as Open Access. The exact amount of open access articles calculated by users of Unpaywall data may vary, depending on which indexes are used to adjust the underlying data. For example, Unpaywall use the DOAJ and look at patterns in their data. Digital Science (in their product, Dimensions) augment the Unpaywall data by looking at full-text and information sourced from publishers. At Delta Think, we augment the Unpaywall data by overlaying our own information from publishers’ price lists, using multiple indexes and looking for patterns in the data.
How much Open Access is there?
Figure 1 below shows our analysis of the 70+ million “journal article” records3 in the Crossref/Unpaywall data set, looking at the proportion of published output falling under different business models.
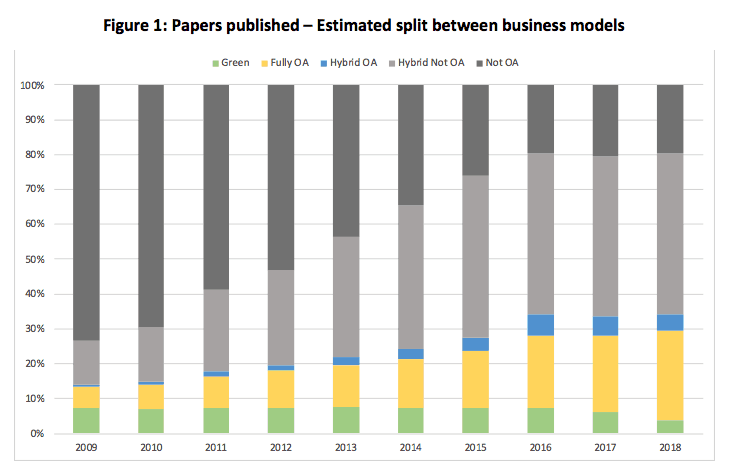
Source: Unpaywall (April 2019 data snapshot), Delta Think analysis.
© Delta Think 2019, All rights reserved.
According to our analysis of the Unpaywall data, across the market as a whole, over one-third of output was published as OA in 2018: 26% in fully OA journals, 5% in hybrid journals and 5% as green.
- Paid Open Access content: The pale blue bars show OA articles in hybrid journals, and yellow shows OA articles in fully OA journals. In 2018 we estimate that they together counted for 31% of output.
- Subscription/Non-OA content: The grey bars show articles which are not OA. These include those which Unpaywall classifies as free-to-read but without permissive license (aka “Bronze”). The light grey shows the proportion of non-OA articles in hybrid journals; the dark grey shows those in journals with no OA option.
- Green Open Access content: In 2018 we estimate articles which are green and off embargo to have been 5% of output. As time goes on, more green articles come off embargo and so we see that green accounts for a higher proportion of output in earlier years. In a year or two’s time we would therefore expect the 2018 proportion of Green to increase (and the proportion of non-OA output to show a corresponding decrease).
- Note: the data set covers around 3.5 million articles published in 2018, growing at an average of 6% per year.
Trends–Year-Over-Year changes
Figure 2, below, focuses on the changing proportions of paid open access over time.
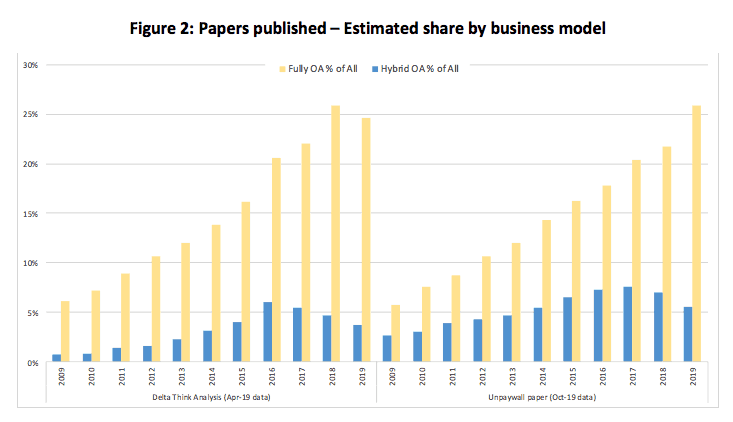
Source: Unpaywall, Delta Think analysis. © Delta Think 2019, All rights reserved.
The left-hand side of the chart shows a different view of the fully OA and hybrid data shown in Figure 1, above.
- Fully OA continues to increase its share of output through 2018.
- However, hybrid OA peaks around 2016, and then shows a decline in share of output.
This suggests that, in terms of share of output, we have passed “peak hybrid.”
- This is a significant finding, so we sense-checked our results against the most recent data from the Unpaywall team (as used for their most recent pre-print). Our comparison is shown in the right-hand side of Figure 2, and shows a similar result, albeit one year later.
- This difference in phasing is likely to do with the differences in underlying methodologies used to relate article output back to parent journal business models. Journal business models may change during a calendar year. Our analysis is designed to anticipate trends. We weight partial-year business models towards the previous year to get a sense of what will be observed through the coming year.
- 2019 readings are partial year’s information. They do not pro-rate linearly through time, but it is likely that the more recent data gives a better read.
Conclusions
Even allowing for different methodologies, like-for-like underlying trends appear consistent. It seems that even before the effects of Plan S have fully manifested, hybrid share of output is slowing. Note that the overall number of hybrid articles continues to grow – it’s just that other content types are growing more quickly.
There could be a number of reasons for this. For example, most of the funders pushing for OA rolled out their mandates over the last few years. We may therefore be seeing a natural slow-down as localized silos of OA uptake are nearing saturation. Meanwhile, until mandates in other areas of the world change or appear, further wholesale shift is unlikely.
Based on the work we have done for publishers and consortia, we know that the patterns of output (of OA and non-OA content) vary by subject area and collection. In particular, the underlying Crossref data does not allow us to separate peer-reviewed content from other types (such as letters or errata). So, trends in one content type may skew the overall trends or mask trends in another.
As ever, we lament that without an industry-standard way of marking articles Open Access, we have to analyze imperfect data. Some terrific tools now exist to help us do this, but bridging the underlying gaps still requires an element of judgement.
Further deep analysis of the data lies outside the scope of this piece. But we leave you with one thought. If hybrid share is already in decline, but transformative agreements are on the rise, then will Plan S have the effect of slowing down the very change it’s trying to accelerate?
1 “Unpaywall is an open source application that links every research article that has been assigned a Crossref DOI (more than 100 million in total) to the OA URLs where the paper can be read for free. It is built and maintained by Our Research (formerly Impactstory), a US-based nonprofit organization.”
2 The Unpaywall study is Piwowar, Priem and Orr – The Future of OA: A large-scale analysis projecting Open Access publication and readership. (Pre-print.) https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-015-1765-5.
3 Items registered with Crossref may be categorized as “journal-article,” “monograph,” “proceedings” and so on. “Journal-article” is the most fine-grained classification for items in journals, including research articles, reviews, letters, etc. Of the total 110m records in the April 2019 data, around 71m were labelled “journal-article.”

TOP HEADLINES
The MIT Press receives a grant from the Arcadia Fund to develop and pilot a sustainable framework for open access monographs – October 3, 2019
“The MIT Press has received a three-year $850,000 grant from Arcadia, a charitable fund of Lisbet Rausing and Peter Baldwin, to perform a broad-based monograph publishing cost analysis and to develop and openly disseminate a durable financial framework and business plan for open access (OA) monographs.”
Cabells reviews and adds 12,000th publication to its Journal Blacklist – October 2, 2019
“Cabells, the complete source for journal information, evaluation metrics, and submission details for authors, has reviewed and added the 12,000th publication to its Journal Blacklist. The updated database offers Cabells’ users the ability to verify that potential outlets for their research are not deceptive and fraudulent predatory journals.”
Subscribe to Open: A practical approach for converting subscription journals to open access – October 1, 2019
“OA business models must be sustainable over the long term, and article processing charge payments do not work for all; Subscribe to Open (S2O) is proposed, and being tested, as an alternative model.”
ARL Supports University of California Libraries’ Commitment to Barrier-Free Access to Information – September 30, 2019
“ARL appreciates the UC system’s leadership in the broader library community as we individually and collectively create new models to achieve enduring and barrier-free access to information.”
Insights into European research funder Open policies and practices – September 30, 2019
“This report summarises the results of a survey of European research funders on Open Access (OA) and Research Data (RD) policies. Launched in the spring of 2019, the survey, which targeted about 400 funders, garnered just over 60 responses from 29 countries.”
SSP Webinar Recap: Three Perspectives on “Plan S: Opportunities for the Future of Scholarly Publishing” – September 24, 2019
“SSP delivered a webinar discussion that takes Plan S and the movement toward Open Access (OA) as a given. The speakers were then charged with offering business models that would suit the new access landscape.”
Jisc Router agreement with IOP Publishing – September 23, 2019
“A new agreement between IOP Publishing (IOPP) and Jisc will enable the provision of journal articles published on a gold open access basis directly to institutional repositories in the UK. Using a service called the Jisc Publications Router, IOPP will pass published articles, in their final published versions, directly to the correct institutional repositories of their authors.”
Portico access alert: 3 OA titles from Veruscript – September 19, 2019
“The Portico archive now hosts the content from three open access e-journals published by Veruscript:Cambridge Journal of Eurasian Studies, Journal of Intelligence and Terrorism Studies, and Veruscript Functional Nanomaterials. Veruscript ceased operations in May 2019 and these three journals were no longer hosted by any online platform; therefore, they have ‘triggered’ and are available to the community via the Portico archive.”
OA JOURNAL LAUNCHES
October 18, 2019 | “IET Quantum Communication will publish novel research and original survey articles focusing on the application of quantum information science to provide the security and infrastructure for future communication networks.” | |
October 17, 2019 | “Oxford University Press (OUP) is pleased to announce the launch of Neurosurgery Open, published on behalf of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons (CNS). Neurosurgery Open is an online-only, fully Open Access publication. The first articles will publish in January 2020 and from then, content will publish on a rolling basis with issues closed quarterly.” | |
October 16, 2019 | Bentham Science launches the journal New Emirates Medical Journal | “Bentham Science is pleased to announce the launch of the Open Access journal, New Emirates Medical Journal. The first issue of the journal, by Bentham Science, will be available online by the start of the year, 2020.” |
October 15, 2019 | New journal to explore the ‘mysterious ecosystem’ in our gut | “A new open access journal from Cambridge University Press, Gut Microbiome, published in partnership with The Nutrition Society, will explore the vital interaction between people and the complex community of microorganisms that live in our digestive systems.” |
October 1, 2019 | Materials Research Expresschanges to a fully gold Open Access journal | “In response to increasing community demand for more accessible and open science, IOP Publishing’s Materials Research Express (MRX)has now changed to a fully gold Open Access (OA) journal funded by article publication charges (APCs), with immediate effect for all new article submissions.” |
September 27, 2019 | “Frontiers in Digital Health publishes rigorously peer-reviewed research in all major digital health science disciplines — from mobile applications to personalized medicine.” | |
September 25, 2019 | “Starting 17 October, the AGU journal Space Weather: The International Journal of Research and Applications (SWE) will transition to an open access model with all articles accepted after that date accessible free of charge to readers.” |